| |
| |
| Discovering Windows Default Password Using LsaRetrievePrivateData |
| |
| |
|
|
|
| |
| |
|
Windows provides Security Management
functions [ Reference
1] for managing various Windows
secrets. One such function is LsaRetrievePrivateData [ Reference
2] which
retrieves various secret data from system policy that has been
previously stored using the
function LsaStorePrivateData. One of the secret data stored by this
function is the 'DefaultPassword'.
All this secret information is
stored in the encrypted format at system location in the registry.
Normally these registry keys are not visible even if you run regedit
as administrator. You need to use any of the techniques as described
in this article [ Reference 3] to view these secret keys.
Here is the screenshot of Regedit.exe running under system account showing
the 'DefaultPassword' secret key.
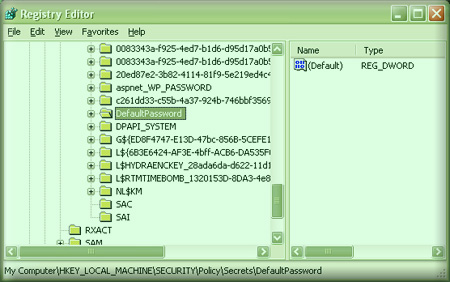
|
| There are lot of other Lsa secret strings which are present at
below registry location |
| HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Security\Policy\Secrets |
| |
| |
|
We don't have to manually decrypt this 'DefaultPassword' value
from the registry to
get the clear text password. The LsaRetrievePrivateData function does it
in style without much work.
Here is the code snippet which illustrates how to use
LsaRetrievePrivateData to retrieve the default logon password. |
| |
| Before we begin, we need to open a handle to LSA policy. |
|
//Open the handle to LSA Policy
if( LsaOpenPolicy(NULL, &ObjAttributes, POLICY_ALL_ACCESS, &hLsaPolicy)
!= STATUS_SUCCESS )
{
printf("\n LsaOpenPolicy failed");
return;
} |
| |
Once the handle is opened, proceed to retrieve the default password
by directly invoking function LsaRetrievePrivateData
|
|
PLSA_UNICODE_STRING privateData = NULL;
WCHAR wstrKeyName[]=L"DefaultPassword";
LSA_UNICODE_STRING keyName;
keyName.Buffer = wstrKeyName;
keyName.Length = wcslen(wstrKeyName) * sizeof(WCHAR);
keyName.MaximumLength = (wcslen(wstrKeyName) + 1) * sizeof(WCHAR);
if( LsaRetrievePrivateData(hLsaPolicy, &keyName, &privateData) !=
STATUS_SUCCESS)
{
printf("LsaRetrievePrivateData failed");
return;
} |
| |
On successful execution, display the retrieved default password and
close the handle
|
printf("\n Success : default password is %S (%d)",
privateData->Buffer, privateData->Length);
LsaClose(hLsaPolicy); |
| |
| This is straightforward code to get the 'defaultpassword'. Also note
that you need to have administrator privileges for this code to execute
successfully.
|
| |
| |
|
Though this method is deprecated since XP onwards it still works
even on Windows 7. However it is not necessarily have to be current logon
user password as there is only one 'DefaultPassword' setting for entire
system.
Also its not clear under what conditions this password get saved and
what password gets stored.
Though its not reliable method for applications to get the logon
password, it may get you the right password sometimes. |
| |
| |
|
| 1.
Windows Security Management Functions |
|
2. MSDN - LsaRetrievePrivateData API Function |
|
3. Discovering hidden registry keys in Windows |
| |
| |
|
|
|
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |
| |